State-of-the-art GenitoUrinary Cancers at The Angeles Clinic and Research Institute
Genitourinary (GU) cancers are a group of cancers that affect the organs of the urinary system and the male reproductive system. These cancers include bladder cancer, testicular cancer, prostate cancer, and renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer).
In general, treatment for genitourinary cancers often involves a multidisciplinary approach, with a team of specialists working together to develop a personalized treatment plan for each patient. This may include urologists, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other healthcare professionals. The goal of treatment is to effectively destroy cancer cells while preserving as much healthy tissue and organ function as possible, while minimizing the risk of complications and side effects.
At The Angeles Clinic and Research Institute patients are offered state-of-the-art multi-disciplinary care and first in class therapeutics for the diagnosis and treatment of their diagnosis. Our physicians and clinical staff are globally recognized and leaders in the field who complement the practice of treating patients with some of the most innovative clinical trials in the world to help further progress professional knowledge in the fight against cancer.
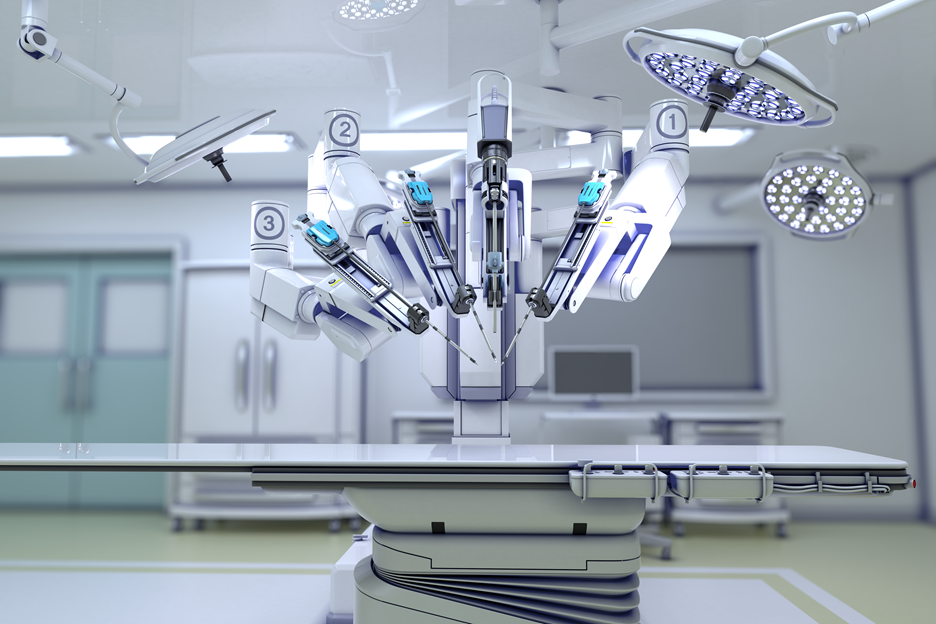
Minimally invasive surgery with DaVinci.
Minimally invasive surgery with the DaVinci robo is a surgical technique that uses a robotic system to perform surgery through small incisions in the body. This technique is particularly useful for treating GU (genitourinary) cancers such as prostate, bladder, and kidney cancers. For GU cancers, DaVinci surgery may be used to remove tumors, repair damaged tissues, or reconstruct the urinary system. This type of surgery is typically performed by a urologist or a surgical oncologist who has received specialized training in using the DaVinci system.
During a DaVinci surgery, the surgeon sits at a console and operates the robotic arms, which are equipped with miniature surgical instruments and a high-definition camera. The camera provides a clear, magnified view of the surgical area, allowing the surgeon to perform precise movements with greater control and dexterity than traditional open surgery. One of the main benefits of minimally invasive surgery with DaVinci is that it typically results in less pain, bleeding, scarring, and a shorter recovery time compared to open surgery. Additionally, this technique may reduce the risk of infection and other complications associated with traditional surgery.
HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound)
HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound) is a minimally invasive treatment option for prostate cancer. It uses high-frequency sound waves to heat and destroy cancer cells in the prostate gland. During the HIFU procedure high-intensity ultrasound waves are delivered that target the cancerous tissue in the prostate. The ultrasound waves create heat, which destroys the cancer cells while leaving the healthy tissue around the prostate intact.
HIFU is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, meaning the patient can go home on the same day. Recovery time is relatively short, and most patients can return to their normal activities within a few days. One of the main advantages of HIFU is that it is a non-invasive procedure that does not require surgery, incisions, or general anesthesia. It also has a low risk of side effects compared to other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy.
Overall, HIFU is a promising treatment option for selected patients with prostate cancer, offering a less invasive and more targeted approach to destroying cancer cells while minimizing the risk of complications.


